How to install Wordpress 4 on Ubuntu 14.04 LAMP
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial Xerus)
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty Tahr)
On this page
This document describes how to install and configure Wordpress 4.0 on Ubuntu 14.04. WordPress started in 2003 with a single bit of code to enhance the typography of everyday writing and with fewer users than you can count on your fingers and toes. Since then it has grown to be the largest self-hosted blogging tool in the world, used on millions of sites and seen by tens of millions of people every day. This tutorial explains the process of installing Wordpress 4.0 on Ubuntu 14.04 in the form of a simple-to-follow guide.
1 Preliminary Note
This tutorial is based on Ubuntu 14.04 server, so you should set up a basic Ubuntu 14.04 server installation before you continue with this tutorial. The system should have a static IP address. I use 192.168.0.100 as my IP address in this tutorial and server1.example.com as the hostname. You must have a LAMP server installed in Ubuntu 14.04 as mentioned in the tutorial to continue further.
2 Database initialization
I will create the database for the Wordpress 4.0 as follows:
mysql -u root -p
Here we are adding database=wordpressdb user=wordpressuser and password=wordpresspassword:
CREATE DATABASE wordpressdb;
CREATE USER wordpressuser@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'wordpresspassword';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON wordpressdb.* TO wordpressuser@localhost;
Further moving ahead:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
exit
Restart services
service apache2 restart
service mysql restart
3 Installation of Wordpress 4.0
We will first make a directory temp in which I will the download the latest version of the Wordpress as follows:
mkdir temp
cd temp
wget http://wordpress.org/latest.zip
We need to install unzip as by default it is now installed:
apt-get install unzip
Further moving ahead if you wish to work with images, install plugins and site updation with SSH credentials then we will install php5-gd libssh2-php
apt-get update
apt-get install php5-gd libssh2-php
unzip the Wordpress zip file in the following created folder:
unzip -q latest.zip -d /var/www/html/
Now give appropriate permissions in the directory
chown -R www-data.www-data /var/www/html/wordpress
chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/wordpress
Further we need to manually create the uploads directory beneath the wp-content directory at our document root. This will be the parent directory of our content:
mkdir -p /var/www/html/wordpress/wp-content/uploads
We need to allow the web server itself to write to this directory. We can do this by assigning group ownership of this directory to our web server. This will allow the web server to create files and directories under this directory, which will permit us to upload content to the server. Proceed like this:
chown -R :www-data /var/www/html/wordpress/wp-content/uploads
Now we need to copy it to the default configuration file location to get WordPress to recognize the file. The sample configuration file is available at /var/www/html/wordpress:
cd /var/www/html/wordpress/
cp wp-config-sample.php wp-config.php
vi wp-config.php
[...]
// ** MySQL settings - You can get this info from your web host ** // /** The name of the database for WordPress */ define('DB_NAME', 'wordpressdb'); /** MySQL database username */ define('DB_USER', 'wordpressuser'); /** MySQL database password */ define('DB_PASSWORD', 'wordpresspassword');
[...]
Change values as you gave at the time of database initialization.
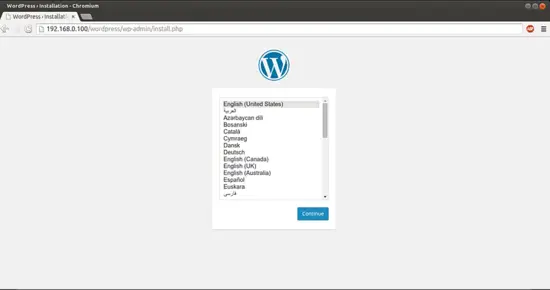
Now proceed to the web installation of Wordpress. Go to the URL http://192.168.0.100/Wordpress:
Select language and press Continue:
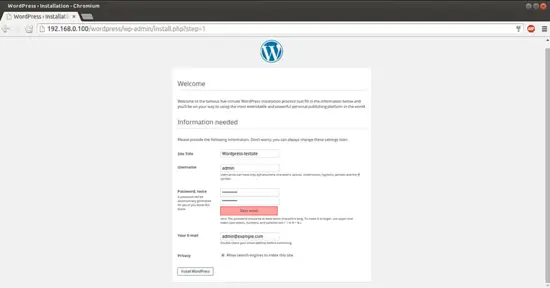
Now give the values as I gave in my case
Site Title = Wordpress-testsite Admin Email = [email protected] Username = admin Admin password = howtoforge Confirm Admin Password = howtoforge
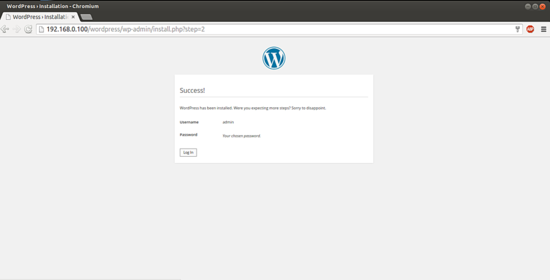
The above values will differ in you case, you can give any values of your choice. After giving the values press InstallWordpress:
Now we will proceed towards the login page by pressing LogIn:
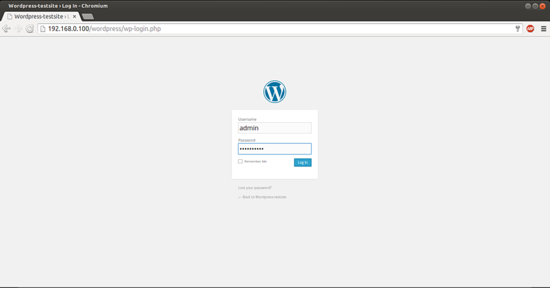
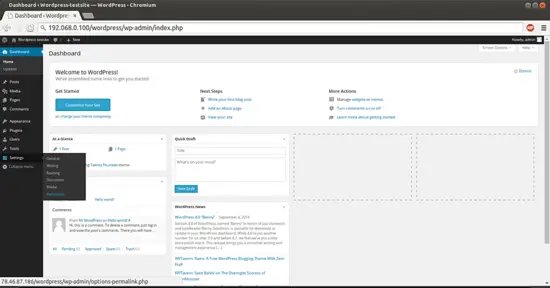
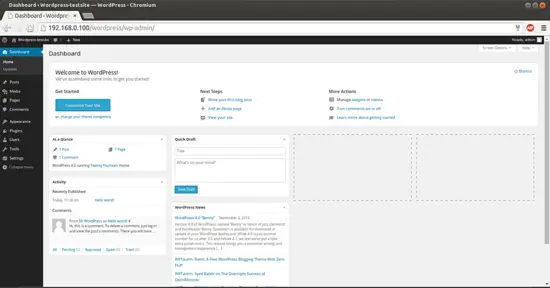
Give the credentials as you selected at the time of web wordpress installation. This will be your default welcome window of Wordpress.
You can check the Wordpress version in browser as: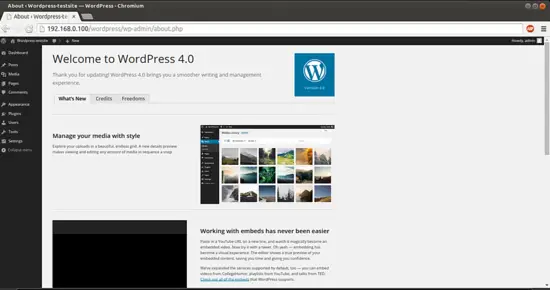
6 Configure Pretty Permalinks for WordPress 4.0
This part is optional.
By default, WordPress creates URLs dynamically that look something like this http://server_domain_name_or_IP/?p=1. This isn't exactly the most useful interface for visitors or search engines, so most users want to modify this. WordPress has the ability to create "pretty" permalinks which will clean up the URL into a more human-friendly format. To overcome this thing we will proceed as follows:
6.1 Apache Rewrite
We will modify the apache virtual host file for Wordpress 4.0 to get it allowed for .htaccess overrides. For this we will edit the virtual host file and add the entries as:
vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf
[...]
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost DocumentRoot /var/www/html ServerName server1.example.com <Directory /var/www/html/> AllowOverride All </Directory> [...]
Next, we need to enable the rewrite module, which allows you to modify URLs. As:
a2enmod rewrite
service apache2 restart
6.2 Create an .htaccess File
Now we will create .htaccess file in document root, it will allow Apache to rewrites:
touch /var/www/html/wordpress/.htaccess
We need the web server to be the group owner though, so we should adjust the ownership as follows:
chown :www-data /var/www/html/wordpress/.htaccess
If you want WordPress to automatically update this file with rewrite rules, you can ensure that it has the correct permissions to do so by using:
chmod 664 /var/www/html/wordpress/.htaccess
If you want to update this file manually for the sake of a small security gain, you can allow the web server only read privileges by typing:
chmod 644 /var/www/html/wordpress/.htaccess
In my case I am using permissions 644.
6.3 Permalink Settings in WordPress
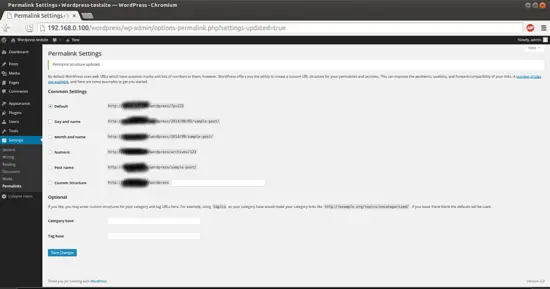
Now we can easily adjust the permalink settings through the WordPress administration interface. Goto Settings-->Permalinks:
When you have made your selection, click "Save Changes" to generate the rewrite rules.
Case1:If you allowed the web server write access to your .htaccess file, you should see a message like this:
Case2: If you did not allow the web server write access to your .htaccess file, you will be provided with the rewrite rules you need to add to the file manually.
Copy the lines that WordPress gives you and then edit file on your server:
vi /var/www/html/wordpress/.htaccess
Just add the lines generated in the file and it will provide the same functionality.
Congratulations! You now have a fully functional WordPress 4.0 instance on your Ubuntu 14.04 :)
7 Links
- Wordpress : http://wordpress.org/
- Ubuntu : http://www.ubuntu.com/