How to Setup Riak KV NoSQL Database Cluster on CentOS 7
Riak is a distributed NoSQL database that offers high-availability, fault tolerance, operational simplicity, and scalability. Riak has been written in Erlang and is part of the 'Basho' product line that includes Riak KV (Key-value), Riak TS (optimized for IoT/Time Series), and Riak CS (Riak Cloud Storage).
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install and configure the NoSQL database Riak KV on CentOS 7 server. We will create the Riak KV cluster with three CentOS servers.
Prerequisites
- 3 Servers CentOS 7
- riak01 10.1.1.10
- riak02 10.1.1.11
- riak03 10.1.1.12
- Root privileges
What we will do
- Install Riak KV on CentOS 7
- Basic Riak KV Configuration
- Setup Riak KV Cluster
- Testing
Step 1 - Install Riak KV on CentOS 7
The first step we will do for this guide is to install the Riak KV packages on all of three CentOS servers, so run all commands in this stage on all servers.
We will install the Riak KV from the package cloud repository and will be using the Riak KV packages for the CentOS 7 server.
Add the repository by running the command below.
curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/basho/riak/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash
The command will download the riak repository and key to the system.
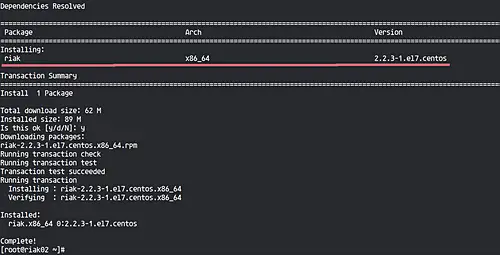
Now install the Riak KV package using the yum command below.
sudo yum install riak-2.2.3-1.el7.centos.x86_64
Wait for the installations.
Step 2 - Basic Configuration Riak KV
In this step, we will configure the Riak KV for our NoSQL cluster. Before configuring the Riak KV itself, we need to set up the open files limit on the Ubuntu system.
Edit the '/etc/security/limits.conf' file using vim editor.
vim /etc/security/limits.conf
Now paste configuration below to the end of the file.
riak soft nofile 65536 riak hard nofile 200000
Save and exit.
Now go to the '/etc/riak' directory, and edit the default configuration file 'riak.conf'.
cd /etc/riak/
vim riak.conf
Change the default nodename 'riak@localhost' with 'riak@ServerIP'.
nodename = [email protected]
Now uncomment those scheduler lines below.
erlang.schedulers.force_wakeup_interval = 500 erlang.schedulers.compaction_of_load = false
Uncomment the 'ring_size' line and leave it to default '64'.
ring_size = 64
Change the HTTP listener and protocol buffers with the 'ServerIP'.
listener.http.internal = 10.1.1.10:8098 listener.protobuf.internal = 10.1.11.10:8087
Save and exit.
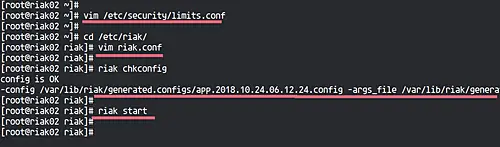
Now test riak configurations, then start the riak service.
riak chkconfig
riak start
Anthe d following is the result.
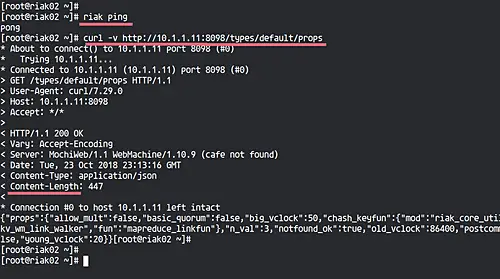
Next, we will test our riak service configuration by running commands below.
riak ping
curl -v http://10.1.1.10:8098/types/default/props
Make sure you get the 'pong' result from the 'riak ping' command and get the HTTP status code '200' from the curl command.
Basic configurations of Riak KV distributed NoSQL has been completed, and we're ready to set up the Riak KV Cluster.
Note:
- Run all commands on this stage on all server nodes.
Step 3 - Setup Riak KV Cluster
In this step, we will set up the cluster by joining the 'riak02' and 'riak03' nodes to the first node.
- Second Node
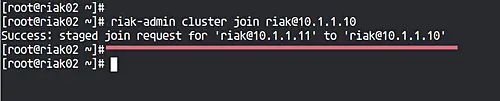
On the 'riak02' node, run the riak-admin below.
riak-admin cluster join [email protected]
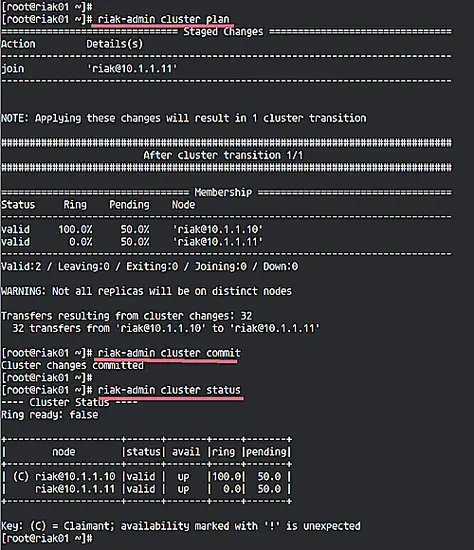
Now back to the 'riak01' node, run riak-admin commands below.
riak-admin cluster plan
riak-admin cluster commit
And the 'riak02' node has been added to the cluster, check it using the command below.
riak-admin cluster status
- Third Node
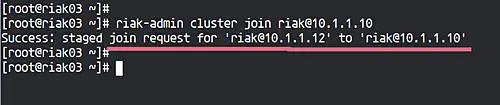
On the 'riak03' node, run the riak-admin command below.
riak-admin cluster join [email protected]
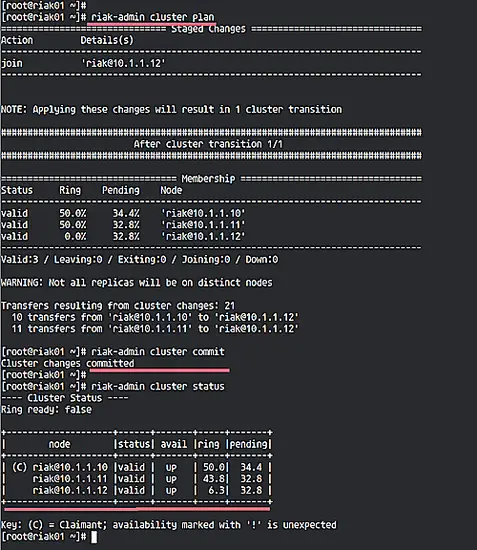
Now back to the 'riak01' node, run riak-admin commands below.
riak-admin cluster plan
riak-admin cluster commit
All server node 'riak02' and 'riak03' has been added to the cluster, check again using the command below.
riak-admin cluster status
The Riak KV cluster installation and configuration has been completed.
Step 4 - Testing
The Riak KV NoSQL cluster has been created, now we want to test the cluster by uploading a data image to the cluster, and test to access from the other nodes to ensure data replication between all nodes.
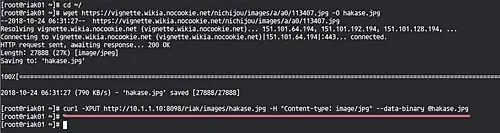
On the 'riak01' server, download an image using the wget command below.
cd ~/
wget https://vignette.wikia.nocookie.net/nichijou/images/a/a0/113407.jpg -O hakase.jpg
Now upload the image to the Riak KV cluster using the curl command.
curl -XPUT http://10.1.1.10:8098/riak/images/hakase.jpg -H "Content-type: image/jpg" --data-binary @hakase.jpg
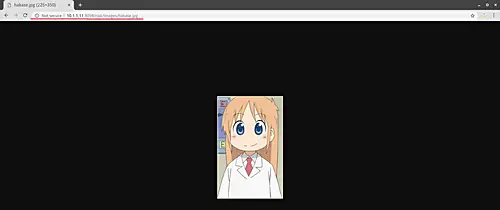
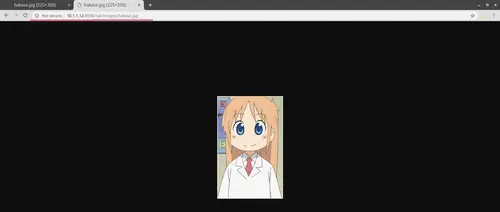
Open your web browser and type other nodes IP address, and you will get the same image.
'riak02'.
http://10.1.1.11:8098/riak/images/hakase.jpg
'riak03'.
http://10.1.1.12:8098/riak/images/hakase.jpg
If you want to delete the image data, use the curl command below.
curl -XDELETE 'http://10.1.1.10:8098/riak/images/hakase.jpg'
The Riak KV Cluster installation and configuration on CentOS 7 has been completed successfully.