So you installed the latest version of a Linux distribution but want to switch to another variant of Linux or want to upgrade to the latest version of a Linux distribution and prefer a clean install over regular upgrade ? Doing this will surely make you lose your personal data. Whether you want to switch between Linux distributions or want to upgrade with a clean install without losing data then you are at the right place. In this article, you will learn how to switch between different Linux distributions without losing data.
Introduction
The first thing you need to do is simply to assign different partitions for your personal data. Keep in mind that this method is for those who are doing a clean install.
The default partition on your hard drive is where your operating system is installed. Usually, Linux installer will create only one partition where all of your personal data is stored alongside the operating system. So whenever you change to a different copy of a Linux distribution, you would have to format this partition. Doing this however means that you will also lose your data. Here is the trick. You simply need to assign a different partition to all of your personal data so that when you format the system partition for a different Linux distribution you won’t erase your data. Just follow the guide below.
Read: Must-do Things After Installing Ubuntu 18.04
While installing a fresh copy of Linux, do the following :
First, create an ext4 partition for the root folder and assign ‘/’ to it as shown in the image below.
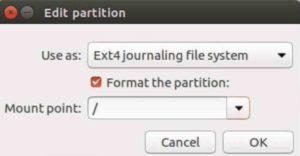
After that, you need to create an additional ext4 partition. This additional partition is used to store all of your personal data. After creating a partition, assign ‘/home’ to it as shown below.
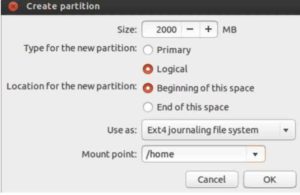
Read: Best Partition Managers for Linux Users
Done, you are all set. Just go ahead and install it. Now whenever you want to switch to a different version of Linux distribution, you simply have to format the system partition and then install a different version of Linux onto that partition. In this process, only system files and your applications are deleted and all of your other data will remain unaltered.
What if a Linux distribution is already installed on my pc?
If you have already installed a copy of Linux in your machine, you probably don’t have a different partition to save your data. You will be able to save your personal data by following this guide. You would need to have basic knowledge of Linux and a working mind in order to copy-paste some commands. This method is a bit more difficult than the previous one, just follow the guide provided below:
- Download the ‘Live bootable ISO’ of your favorite Linux distribution.
- Create a bootable USB drive or burn the content of ISO to a CD/DVD. USB is more convenient and available to everyone.
- Boot into Linux through the bootable media. (you need to boot into Linux through a live bootable media because you cannot resize a partition while booting through regular media)
- Now with the help of partition tools like GNOME disk utility or GParted, resize your existing system ext4 partition to the size you want. For example, by using GParted:
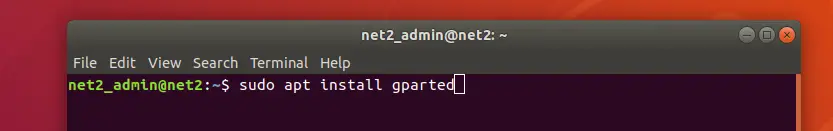
If it shows an error then install it first using the following command:
sudo apt install gparted
Read: How to Use CDC to Optimize Your ELT Process
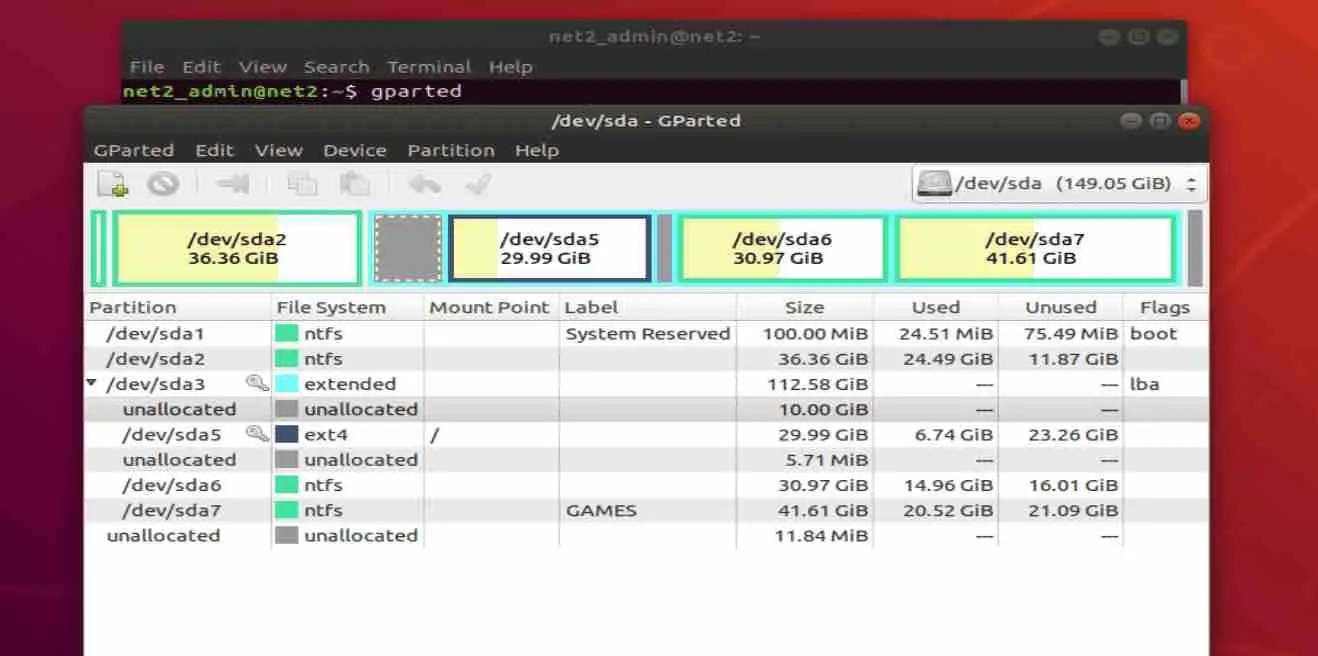
- Now an empty space is created because of the resizing of the first partition. Create a new ext4 partition out of that empty space.
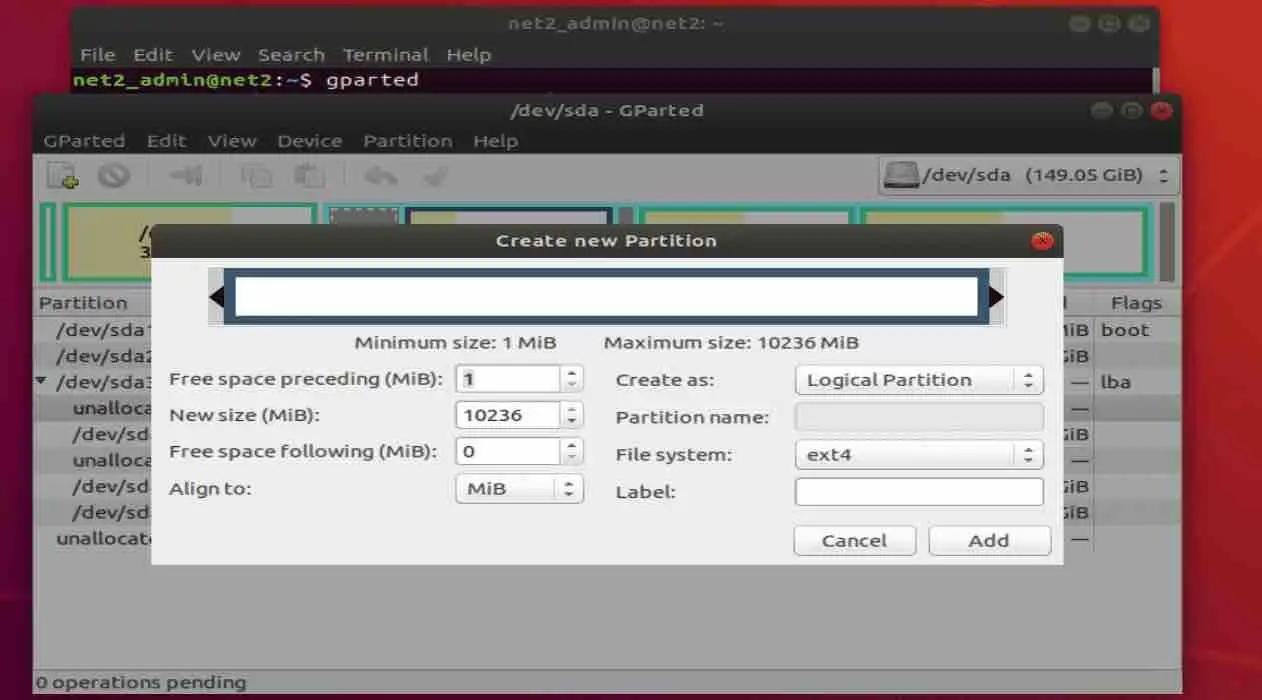
- It should look like /dev/sdxy, here, “x” is assigned to the drive and “y” is assigned to partition. Keep this in mind if it is used again.
- Copy the content of “/home” folder to the new partition.
- Now open the terminal and run the following command to open the gedit text editor:
gksudo gedit
- Now use the menu to open the file at the location /etc/fstab in the system partition.
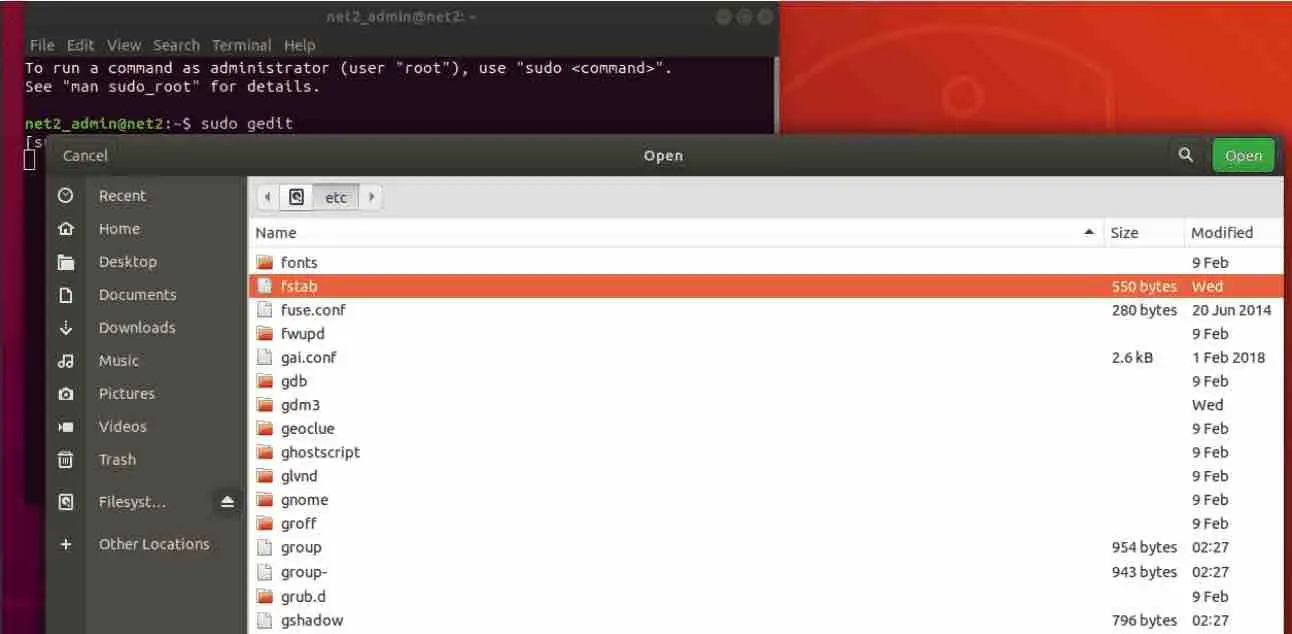
- Copy the following line and paste it at the end of the file as shown in the screenshot and don’t forget to replace “x” and “y”.
/dev/sdxy /home errors=remount –ro 0 1
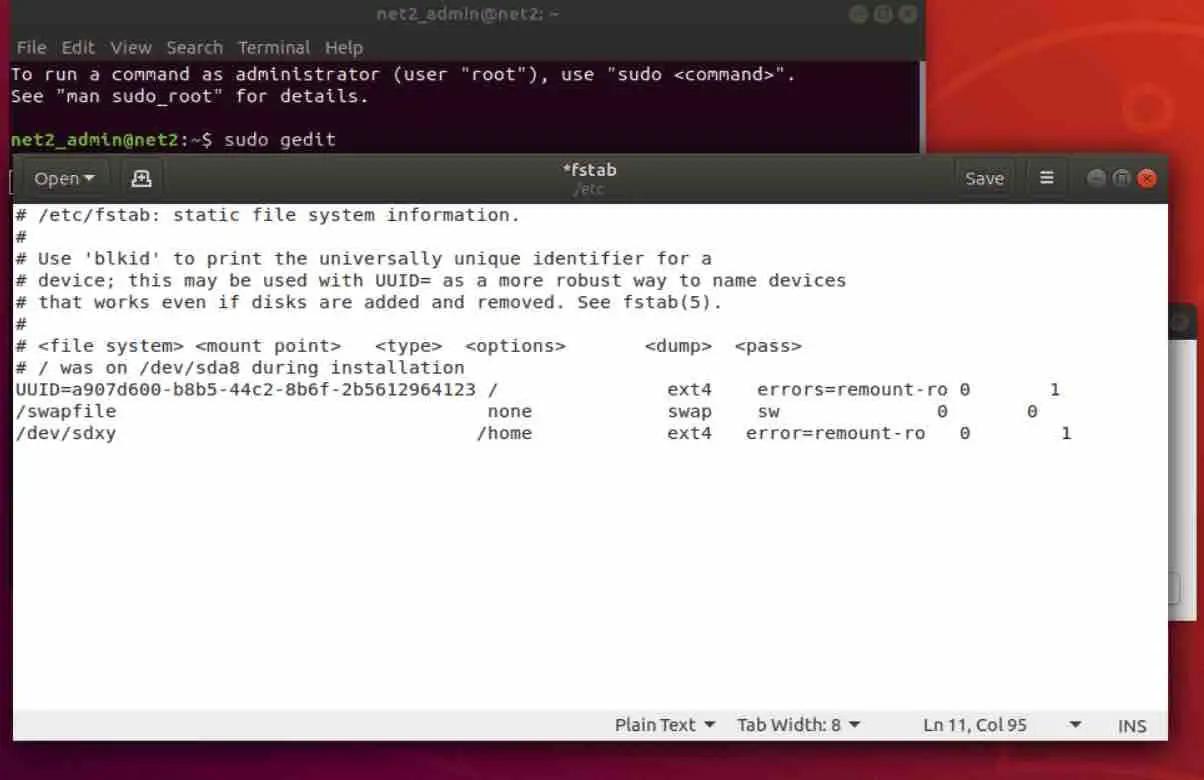
- Save the file and restart. Remove the live bootable media and boot normally.
Done ! now you are all set to switch to any other copy of Linux on your machine without losing your data.
Things that you should keep in mind.
After changing to a different distribution of Linux, your application will be deleted but their settings will remain saved with your personal data so that you don’t have to reconfigure them. Switching between different distributions of Linux may cause incompatibility issues. So if you encounter any problem after switching, then do a fresh install. Give the new partition enough room so you can save all of your files. Only copy the content “/home” folder and don’t copy the “/home” folder itself.
If you like the content, we would appreciate your support by buying us a coffee. Thank you so much for your visit and support.



“Only copy the content “/home” folder and don’t copy the “/home” folder itself.”
You mean “In this case, only copy the contents of/in the “/home” folder, but don’t copy the “/home” folder itself, as there should be only one /home folder.”, right?
only the content would need to be copied