How to Install Nextcloud on Rocky Linux
On this page
- Prerequisites
- Installing Apache/Httpd Web Server
- Installing PHP on Rocky Linux
- Installing and Configuring MariaDB
- Creating Database for Nextcloud
- Download Nextcloud Source Code
- Enable Apache/Httpd mod_ssl Module
- Generating SSL Letsencrypt with Certbot
- Setting Up Apache Virtual Host for Nextcloud
- Installing Nextcloud
- Nextcloud Performace Tuning
- Conclusion
Nextcloud is free and open-source software that allows you to create file hosting services like Dropbox, Google Drive, or Mega.nz. It's created by the original owncloud developer Frank Karlitschek. In 2016, he forks the Owncloud project and creates a new project with the name "Nextcloud".
By this time, the Nextcloud project growing rapidly and become more than file hosting software. With the support of a lot of plugins, Nextcloud becomes such a Collaboration software. You can install plugins for project management, video conferencing, collaborative editing, note-taking, email client, etc.
In this guide, you will learn how to install Nextcloud on the Rocky Linux 8.4. You will be installing Nextcloud under the LAMP Stack (Linux, Apache2/httpd, MySQL/MariaDB, and PHP).
Prerequisites
- A Rocky Linux server. Ensure all packages are updated to the latest version.
- A user with root privileges. This user will get the root privileges through the sudo command.
Installing Apache/Httpd Web Server
At first, you will be installing the Apache or httpd web server on the Rocky Linux server.
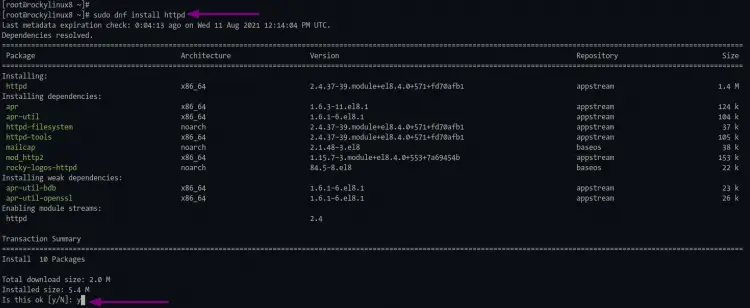
1. Execute the dnf command below to install the httpd web server.
sudo dnf install httpd
Type "y" and press "Enter" to confirm and install httpd packages.
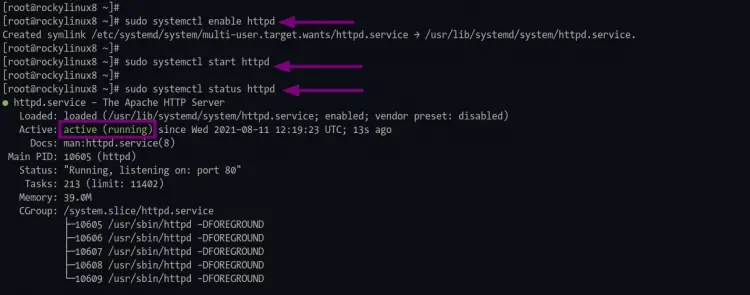
2. If the installation is complete, enable and start the httpd service using the following command.
sudo systemctl enable httpd
sudo systemctl start httpd
The "systemctl enable" command will enable the service to start at every boot.
3. After that, run the command below to verify the httpd service.
sudo systemctl status httpd
And you will get a similar result as below.
As seen on the top screenshot, the httpd is active and running.
Installing PHP on Rocky Linux
As for now, Nextcloud needs PHP 7.4 or higher for the installation. Now you will be installing PHP 7.4 from the remi repository.
1. Execute the following command to add epel and remi Repository
sudo dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm
sudo dnf install https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-8.rpm
Type "y" and press "Enter" to add the epel and remi repository.
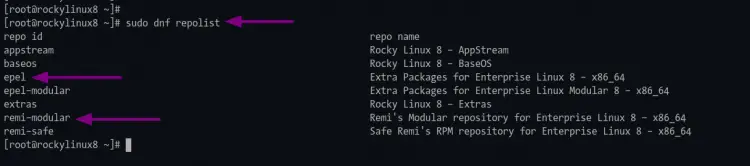
When the installation is complete, verify the epel and Remi repository using the following command.
sudo dnf repolist
You will see the epel and remi repository on the repository list.
2. Next, reset the default repository module PHP. Then enable the module for PHP 7.4 from the remi repository.
Execute the following command to reset the default php module repository.
sudo dnf module reset php
In the process, type "y" and press "Enter" to add the gpg key remi repository.
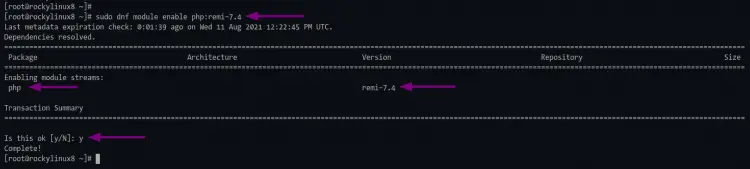
After that, execute the command below to enable the php module from the remi repository.
sudo dnf module enable php:remi-7.4
Type "y" to confirm and press "Enter" to continue. Now you're ready to install PHP and all extensions for the WordPress installation.
3. Execute the following command to install php with some necessary extensions.
sudo dnf install php php-ctype php-curl php-gd php-iconv php-json php-libxml php-mbstring php-openssl php-posix php-session php-xml php-zip php-zlib php-pdo php-mysqlnd php-intl php-bcmath php-gmp php-imagick php-apcu
4. After PHP installation is complete, edit the configuration "php.ini" using nano editor.
nano /etc/php.ini
Change the default value with the configuration below.
file_uploads = On
allow_url_fopen = On
memory_limit = 512M
upload_max_filesize = 500M
post_max_size = 600M
max_execution_time = 300
display_errors = Off
date.timezone = Europe/Amsterdam
Press "Ctrl+x" and type "Y" to save the configuration and exit.
The important configuration you must know:
- For Nextcloud production, you need the "memory_limit" more than 512MB.
- The "upload_max_filesize" option allows you to set up the maximum size upload to your Nextcloud server.
- The "post_max_size" option must be higher than "upload_max_filesize" option.
- The "date.timezone" option must match the system local time "/etc/localtime".
- Increase the "max_execution_time" depending on your server load.
5. Next, change the working directory to "/etc/php.d/" and edit the configuration "10-opcache.ini" using nano editor.
cd /etc/php.d/
nano 10-opcache.ini
Add the following configuration to enable the PHP opecache plugin.
opcache.enable = 1
opcache.interned_strings_buffer = 8
opcache.max_accelerated_files = 10000
opcache.memory_consumption = 128
opcache.save_comments = 1
opcache.revalidate_freq = 1
Press the "Ctrl+x" button and type "Y" to save the configuration and exit.
6. To apply a new PHP configuration, restart the httpd service using the following command.
sudo systemctl restart httpd
Installing and Configuring MariaDB
For this stage, you will be installing the mariadb database server, securing mariadb deployment, and creating a new database and user for Nextcloud.
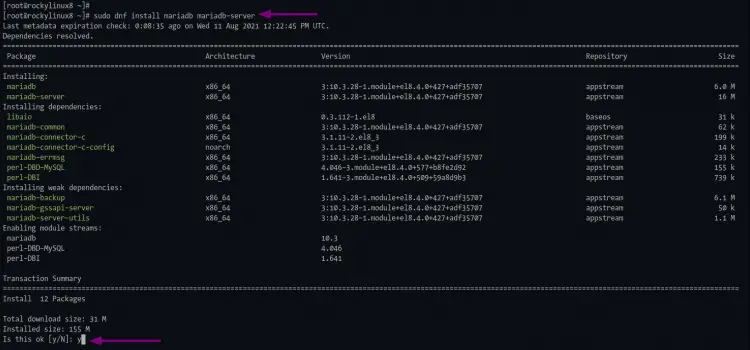
1. To install the mariadb database server, run the command below.
sudo dnf install mariadb mariadb-server
Wait for the mariadb installation.
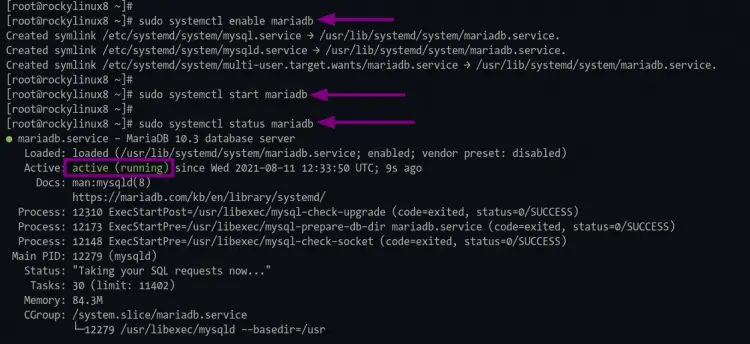
2. Once the installation is complete, enable and start the mariadb service using the following command.
sudo systemctl enable mariadb
sudo systemctl start mariadb
4. The mariadb will be active and running, execute the following command to verify the mariadb service.
sudo systemctl status mariadb
If the mariadb service is running, you will get similar output as below.
5. Next, you need to secure your mariadb deployment by setting up the root password for mariadb and remove some default configuration. To do that, you can use the command-line tool 'mysql_secure_installation', which is included on the default mariadb installation.
Execute the "mysql_secure_installation" command below.
mysql_secure_installation
At the first, you will be asked to set up the mariadb root password.
Type your strong mariadb root password and repeat, then press "Enter" to continue.
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] Y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
Now type "Y" and press "Enter" to remove the default anonymous user from the mariadb server.
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
After that, disable the remote login for the default user 'root'. Type "Y" and press "Enter" to continue.
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
Type "Y" again to remove the default database "test" and press "Enter".
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
And the last, type "Y" again to reload all tables privileges to apply a new configuration.
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
Now the process is complete and you will see the following output.
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
Creating Database for Nextcloud
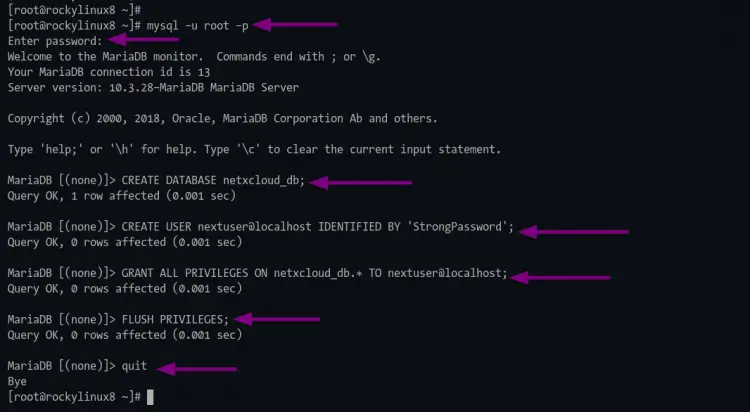
1. log in to the mariadb shell using the mysql command below.
mysql -u root -p
2. Now execute the following mysql query to create a new database "nextcloud_db".
CREATE DATABASE netxcloud_db;
3. Execute the following query to create a new database user "nextuser". Change the "strongpassword" with your strong password.
CREATE USER nextuser@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'StrongPassword';
4. Allow the user "nextuser" to access and write the "nextcloud_db" using the following query.
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON netxcloud_db.* TO nextuser@localhost;
5. Now reload all tables privileges to apply the new database configuration.
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Then you can type "quit" and press "Enter" to exit from the mariadb shell.
Download Nextcloud Source Code
1. Change the working directory to "/var/www" and download the latest version of Nextcloud source code using the wget command as below.
cd /var/www/
wget https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/nextcloud-22.1.0.zip
2. Extract the Nextcloud source code "nextcloud-xx.zip" and you will get a new directory "nextcloud", then change the owner of the "nextcloud" directory to "apache" user.
unzip nextcloud-22.1.0.zip
chown -R apache:apache nextcloud
Now you're ready to configure the httpd virtual host for Nextcloud.
Enable Apache/Httpd mod_ssl Module
For this tutorial, you will be installing Nextcloud and securing with the SSL from Letsencrypt. So you need to enable the mod_ssl for the httpd server on the Rocky Linux.
1. Install the package "mod_ssl" using the dnf command below.
sudo dnf install mod_ssl mod_http2
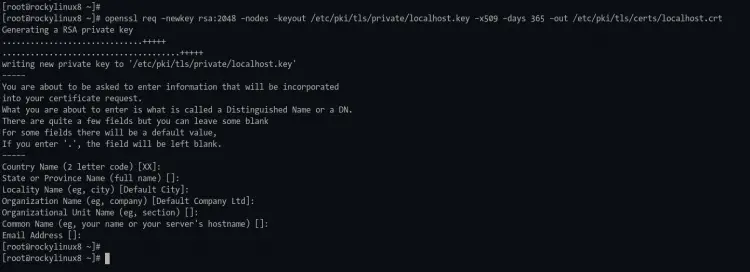
2. after that, generate the default SSL for localhost using the openssl command below. But if you already have certificates "/etc/pki/tls/private/localhost.key" and "/etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.crt", you can skip this stage.
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout /etc/pki/tls/private/localhost.key -x509 -days 365 -out /etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.crt
You can just press enter for all questions because this certificate will only be used for localhost, not the WordPress domain name.
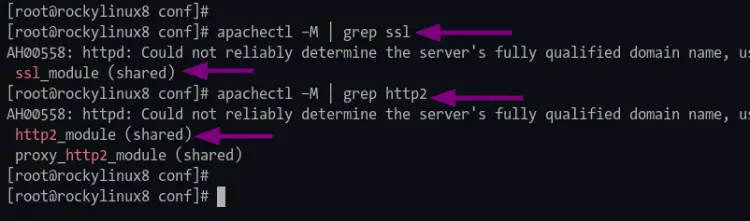
3. Now execute the following command to ensure the mod_ssl is available on the httpd web server.
apachectl -M | grep ssl
If you have got the output such as "ssl", then the mod_ssl is enabled. Otherwise, you will get blank output.
Generating SSL Letsencrypt with Certbot
In this stage, you will be installing the cerbot tool and generate the SSL certificates for the WordPress installation. You will be generating SSL Letsencrypts with the webroot plugin.
1. Execute the following command to install the certbot tool for generating SSL Letsencrypt.
sudo dnf install certbot
Wait for the installation process.
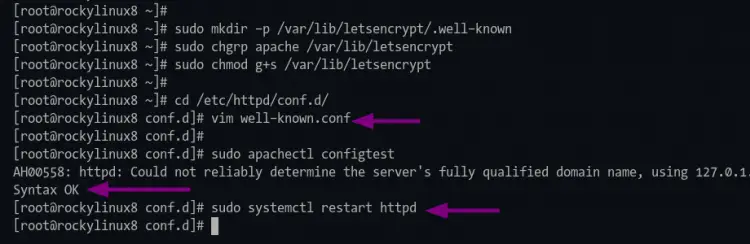
2. Once the installation is complete, create a new directory for letsencrypt authorization using the following commands.
sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/letsencrypt/.well-known
sudo chgrp apache /var/lib/letsencrypt
sudo chmod g+s /var/lib/letsencrypt
3. Next, change the working directory to the "/etc/httpd/conf.d/" and create a new configuration "well-known.conf" using nano editor.
cd /etc/httpd/conf.d/
nano well-known.conf
Add the following configurations.
Alias /.well-known/acme-challenge/ "/var/lib/letsencrypt/.well-known/acme-challenge/"
<Directory "/var/lib/letsencrypt/">
AllowOverride None
Options MultiViews Indexes SymLinksIfOwnerMatch IncludesNoExec
Require method GET POST OPTIONS
</Directory>
Press "Ctrl+x" and type "y" to save and exit.
4. Now execute the following commands to verify the httpd configuration and restart the httpd service.
apachectl configtest
sudo systemctl restart httpd
If you've no error, you're ready to generate SSL Letsencrypt with the webroot plugin.
5. Before generating SSL Letsencrypt, ensure your domain name is resolved to the server IP address. After that, you can generate SSL Letsencrypt with the webroot plugin by running the certbot command below. Also, change the email address and domain name to your own.
sudo certbot certonly --agree-tos --email [email protected] --webroot -w /var/lib/letsencrypt/ -d files.domain.com -d
When the process is complete, your SSL certificates will be available at the "/etc/letsencrypt/live/files.domain.com/" directory.
Setting Up Apache Virtual Host for Nextcloud
In this step, you will be adding a new apache/httpd virtual host configuration for Nextcloud.
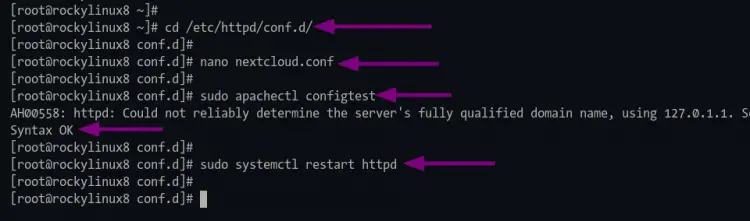
1. Change the working directory to "/etc/httpd/conf.d" and create new configuration "nextcloud.conf" using nano editor.
cd /etc/httpd/conf.d/
nano nextcloud.conf
Change the detail domain name and SSL path directory to your own and paste the configuration to the "nextcloud.conf" file.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName files.domain.com
ServerAlias www.files.domain.com
# auto redirect HTTP to HTTPS
Redirect permanent / https://files.domain.com/
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName files.domain.com
ServerAlias www.files.domain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/nextcloud/
Protocols h2 http/1.1
# auto redirect www to non-www
<If "%{HTTP_HOST} == 'www.files.domain.com'">
Redirect permanent / https://files.domain.com/
</If>
# log files
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/files.domain.com-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/files.domain.com-access.log combined
SSLEngine On
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/files.domain.com/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/files.domain.com/privkey.pem
# HSTS
<IfModule mod_headers.c>
Header always set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=15552000; includeSubDomains"
</IfModule>
<Directory /var/www/nextcloud/>
Options +FollowSymlinks
AllowOverride All
<IfModule mod_dav.c>
Dav off
</IfModule>
SetEnv HOME /var/www/nextcloud
SetEnv HTTP_HOME /var/www/nextcloud
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Press "Ctrl+x" and type "Y" to save the configuration and exit.
3. Next, execute the following command to verify the httpd configuration.
sudo apachectl configtest
If you got no error, restart the httpd service using the command below.
sudo systemctl restart httpd
Now you're ready for the Nextcloud installation through the web browser.
Installing Nextcloud
If all related server configuration is complete, you can access your Nextcloud installation with the web browser.
1. Open your web browser and type the URL address of your Nextcloud installation.
http://files.domain.com
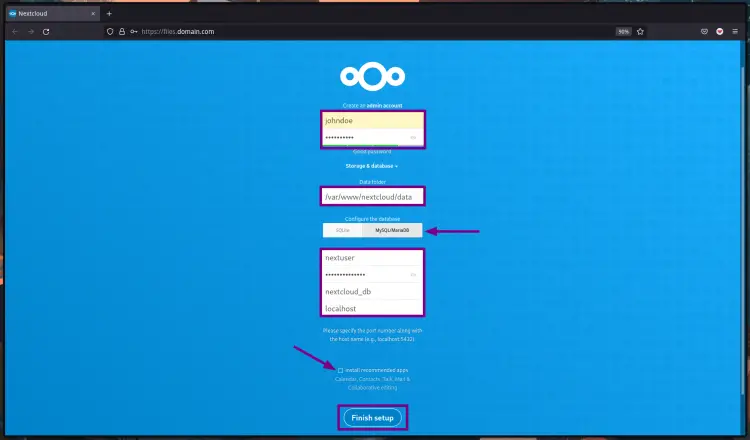
Now you will be redirected to the secure HTTPS connection and you will get the page as follow.
- On the "Create an admin account section", type a new username and password for your admin.
- For the "Data Folder" section, leave it as default by now.
- On the "Configure the database" section, choose "MySQL/MariaDB" and type details database configuration
- Additionally, you can install recommended apps by checking the box option. Or uncheck the box option if you don't want to.
After that, you can click the "Finish setup" button.
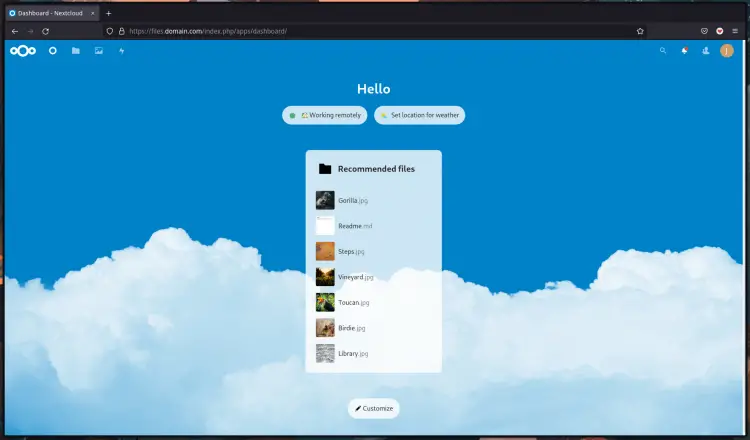
2. After the installation process is complete, you will see the default Nextcloud dashboard as below.
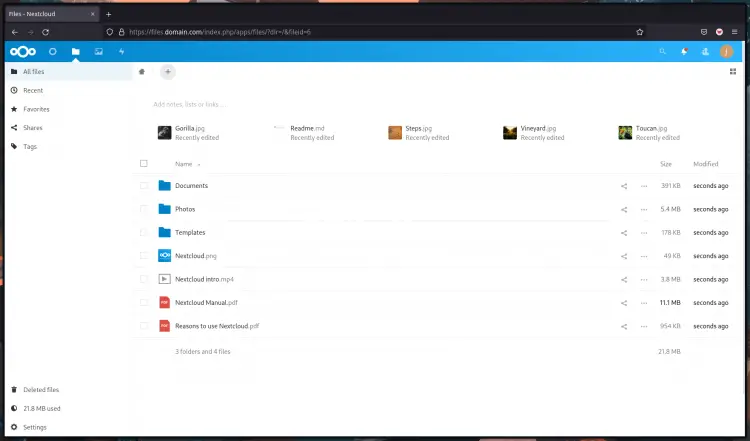
3. Now click the menu "Files" and you will see the user dashboard list of files and folders.
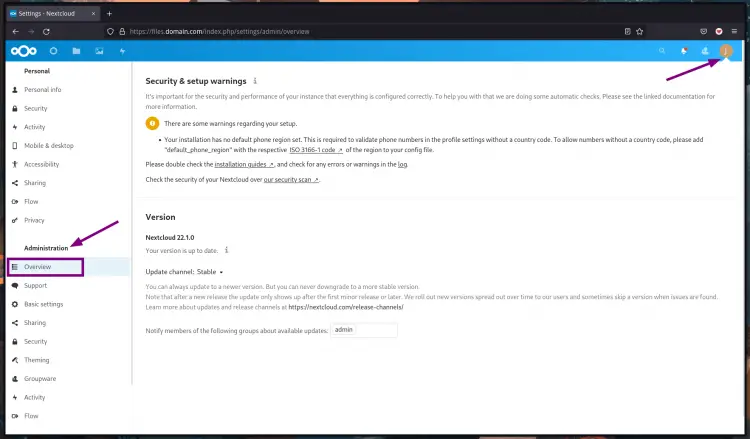
4. To access the administrative page, click the user profile on top and select "Settings".
Under the "Administrative" section, you can change the default Nextcloud configuration.
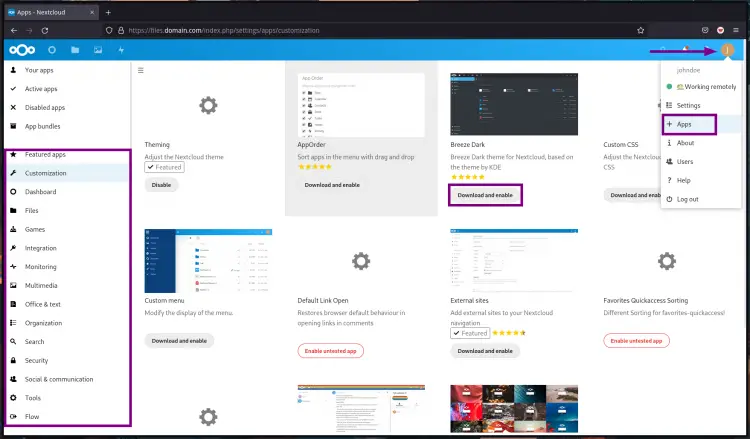
5. To add new plugins or apps, you can click on the user profile on top and select "Apps".
Now you will get the page as follow.
Choose the plugin category that suits you, then click the button "Download and enable". After that, click "Enable" to activate the app or plugin.
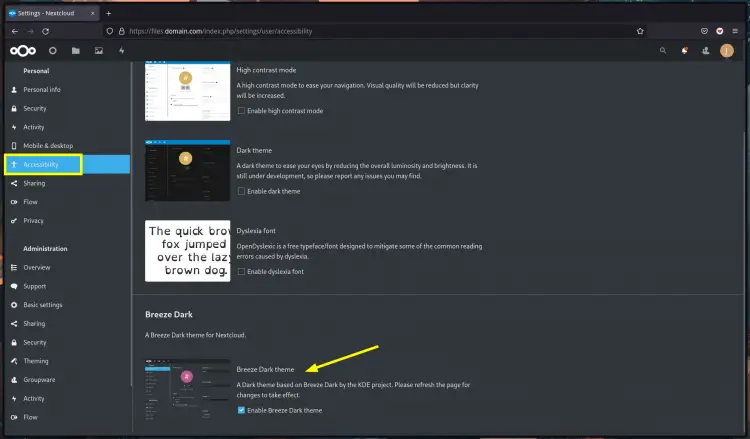
Below is the screenshot after enabling the Nextcloud Breeze Dark theme.
Nextcloud Performace Tuning
After installed Nextcloud, you can do some steps further to increase the Nextcloud performance by enabling the local memory cache and setting up a cronjob for Nextcloud itself.
1. At the top PHP installation section, you already set up the PHP for caching. To enable caching on Nextcloud, edit the Nextcloud configuration "config.php".
Change the working directory to "/var/www/nextcloud/config" and edit the configuration "config.php" using nano editor.
cd /var/www/nextcloud/config/
nano config.php
Add following configuration inside the 'array ( .. );' bracket as below
<?php
$CONFIG = array (
....
....
....
# Additional configuration
'memcache.local' => '\OC\Memcache\APCu',
);
Now press the "Ctrl+x" button and type "y" to save the configuration and exit.
2. A Nextcloud system needs to run some background tasks on regular basis and without any user/admin interaction. To do that, you can use the cronjob for task scheduler Nextcloud tasks.
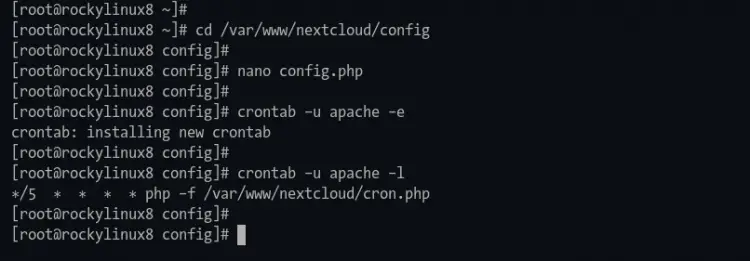
On Rocky Linux, the default httpd user is "apache". Create a new cronjob for user "apache" using the command below.
crontab -u apache -e
Add the following configuration.
*/5 * * * * php -f /var/www/nextcloud/cron.php
Note about configuration and exit.
Cronjob configuration you must know:
- This cronjob configuration allows user "apache" to execute the PHP script "/var/www/nextcloud/cron.php" every 5 minutes.
To verify the cronjob configuration, you can execute the following command.
crontab -u apache -l
If your configuration is a success, you will get the configuration on top as your output. Otherwise, you will get a blank result.
Conclusion
Congratulation! You have successfully installed Nextcloud on Rocky Linux 8.4. The Nextcloud server is running under the LAMP Stack with SSL enabled. Also, your Nextcloud installation is running with memory caching enabled with PHP APC and opcache extensions.