The sudo command allows users to run commands with root privileges. This can be a powerful tool, but it can also be a security risk if not used carefully. One way to mitigate this risk is to allow sudo users to run particular authorized commands. In this guide, we will show you how to restrict sudo users to run specific commands with sudo privileges in Linux. We will also show you how to revert sudoers file back to the original configuration.
Table of Contents
Restrict Sudo Users to Run Authorized Commands
To restrict sudo users to ONLY run authorized commands, you can use the sudoers configuration file. On most Linux distributions, the sudoers file is located at /etc/sudoers file or /etc/sudoers.d/ directory.
Heads Up: Before making changes to the sudoers file, it's crucial to use caution, as incorrect configurations can lead to system issues. Always use the visudo command to edit the sudoers file, as it performs syntax checks before saving changes.
Here's how you can restrict sudo users to run specific commands:
1. It's highly recommended to backup the sudoers file before making any changes or edits to it. To backup sudoers file, run:
$ sudo cp /etc/sudoers /etc/sudoers.bak
By backing up the sudoers file, you can easily revert to a known-working configuration if errors occur during editing or in case of security incidents.
2. Open the sudoers file for editing using visudo command:
$ sudo visudo
3. Scroll down to the line where it says:
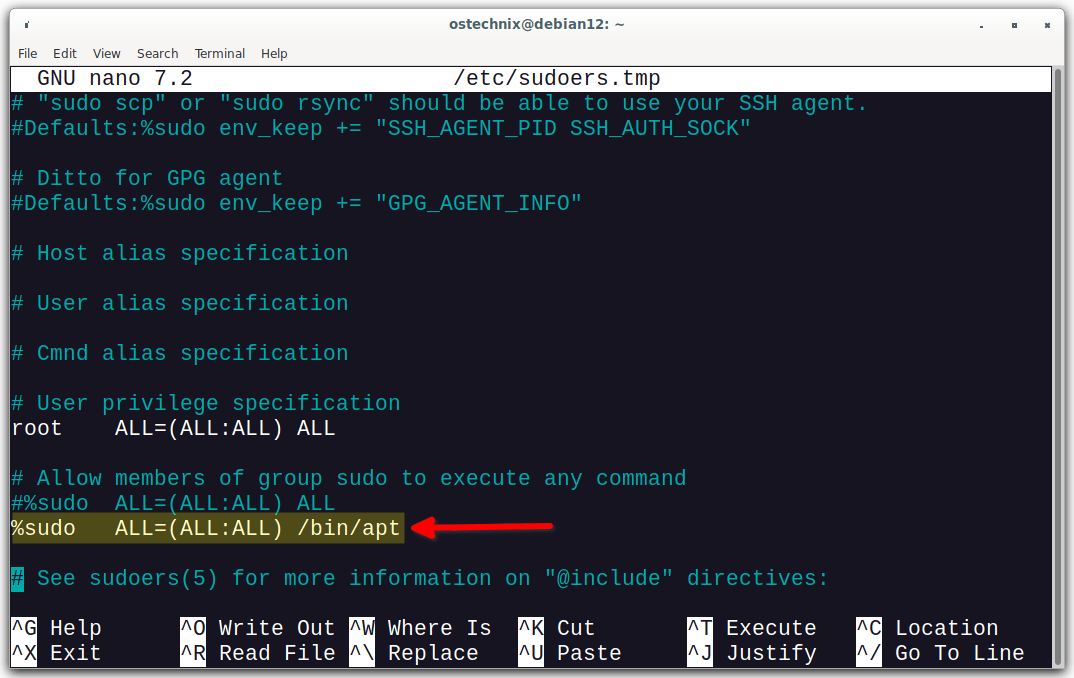
# Allow members of group sudo to execute any command %sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
The above line means that members of the "sudo" group are allowed to execute any command with sudo privileges on any host and as any user or group. Essentially, it grants full sudo access to the users in the "sudo" group.
4. To allow the sudo users to execute only a specific command, for example apt, modify the line as shown below.
%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) /bin/apt
You can also specify multiple allowed commands for a user by separating them with commas:
%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) /path/to/allowed/command1,/path/to/allowed/command2
5. If you want to allow the user to run the allowed commands without entering a password, you can append NOPASSWD: before the command path. However, be cautious when using this option, as it might reduce the security of your system.
%sudo ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /path/to/allowed/command
6. Once you've made the necessary changes, save and close the sudoers file.
7. Verify the syntax of your sudoers file before exiting visudo. If there are any syntax errors, visudo will prompt you to correct them.
After following these steps, all the members of the sudo group will only be able to execute the allowed commands with sudo privileges. Running all other commands with sudo privilege will be denied, even if the user is a member of sudo group.
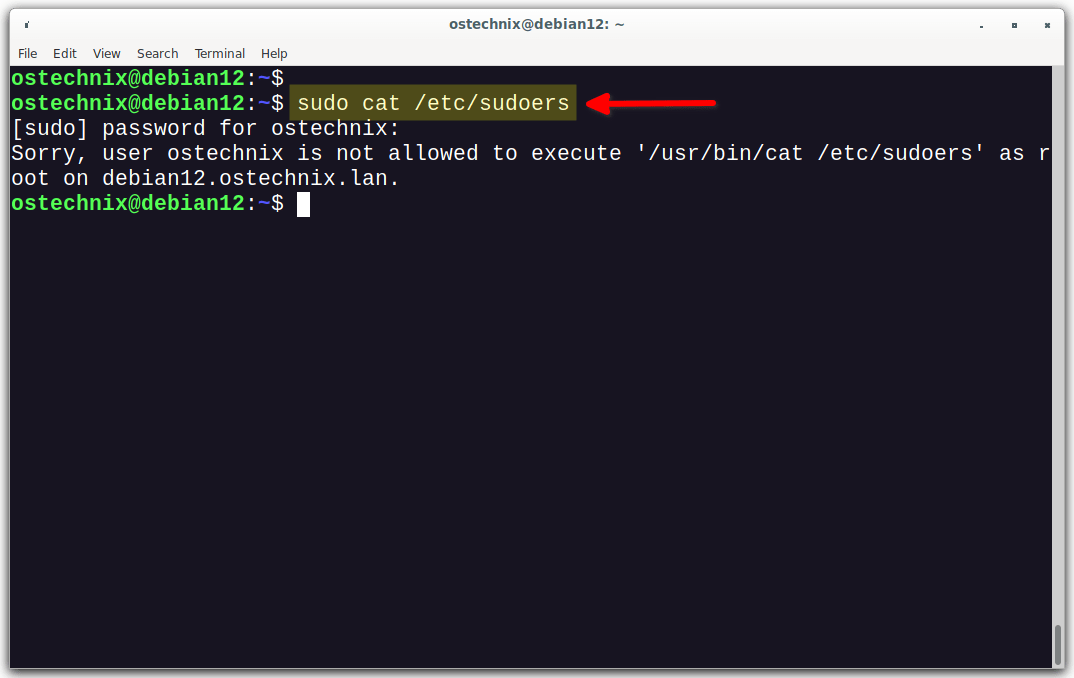
Let us verify it by running the cat command with sudo privilege.
$ sudo cat /etc/sudoers
Sample Output:
[sudo] password for ostechnix: Sorry, user ostechnix is not allowed to execute '/usr/bin/cat /etc/sudoers' as root on debian12.ostechnix.lan.
Even though, the user 'ostechnix' is a member of sudo group, he can't run sudo cat /etc/sudoers command. Because, we restricted him to run only the apt command with sudo privilege.
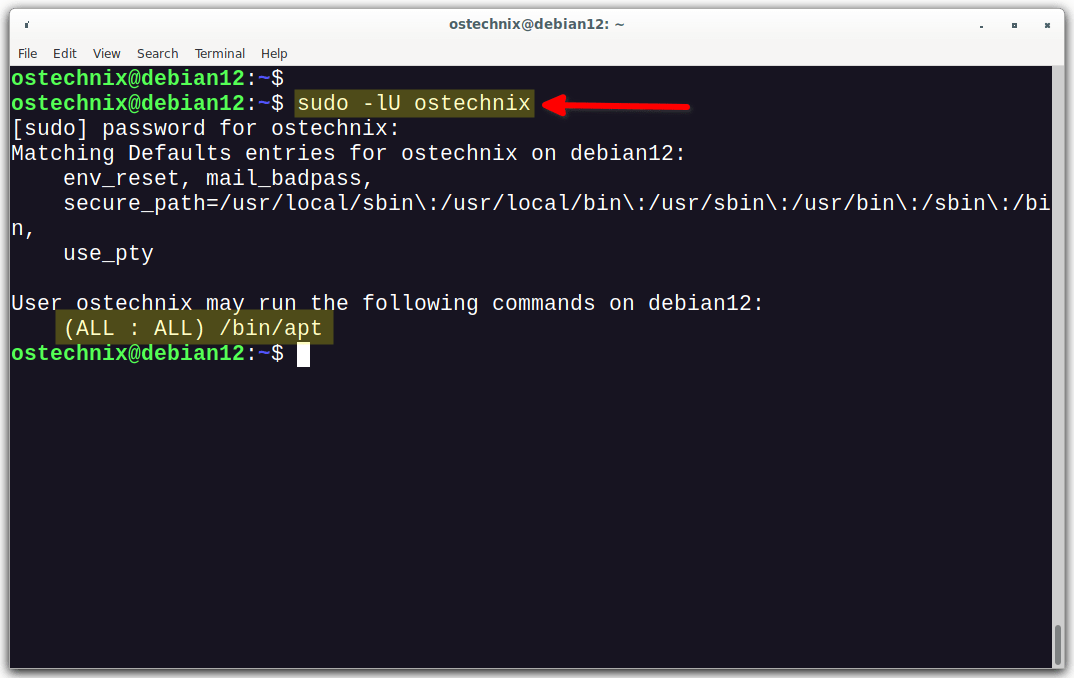
Let us list all of the commands that the user ostechnix is allowed to run with sudo privileges.
$ sudo -lU ostechnix
[sudo] password for ostechnix:
Matching Defaults entries for ostechnix on debian12:
env_reset, mail_badpass, secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin, use_pty
User ostechnix may run the following commands on debian12:
(ALL : ALL) /bin/aptAs you can see in the above output, the user ostechnix can run only apt command with sudo privilege.
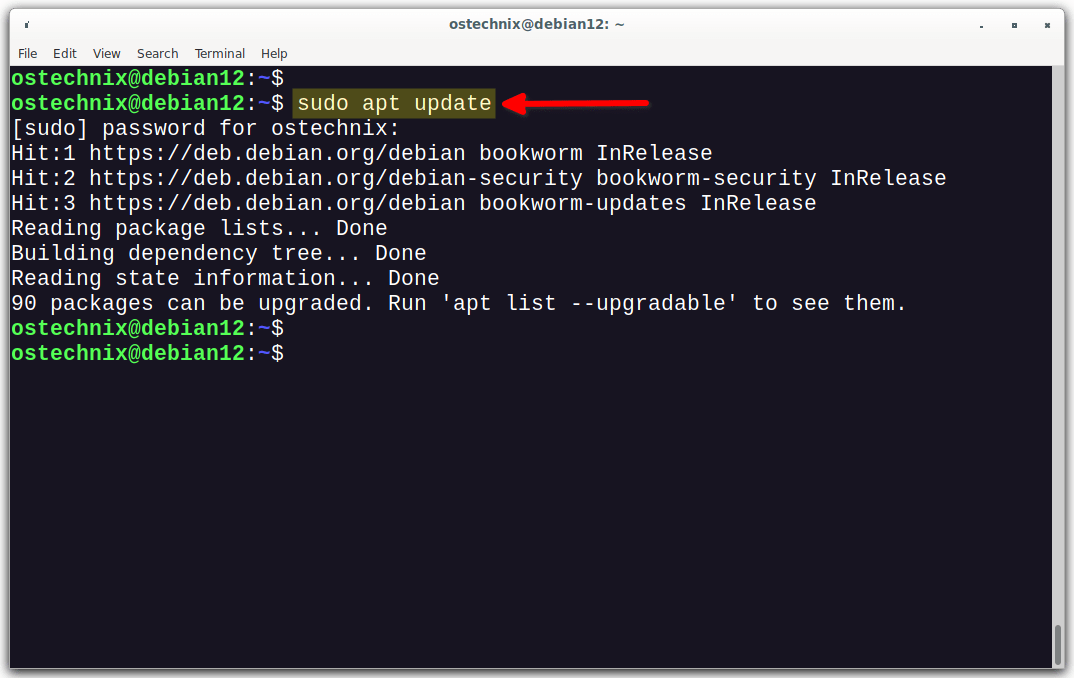
Let us check if he can able to the apt command with sudo privilege.
$ sudo apt update
Yes, he has no problem on running the allowed command, which is apt in this case, with sudo rights. The user can also run all the sub-commands of apt, for example apt upgrade, apt full-upgrade etc.
Please note that this is applicable only for the commands run with sudo privilege. Executing any other commands without sudo will normally work.
Restoring Original sudoers File Configuration
If you want to revert the sudoers file back to the original configuration, you need to change it to the correct syntax that was originally present in the file. To do that, follow these steps:
1. Login as root user or switch to another sudo user who has full sudo privilege.
2. If you already have the backup, restore the sudoers file from the backup using the following command (assuming the backup file is in /etc directory).
$ sudo cp /etc/sudoers.bak /etc/sudoers
If you don't have backup, follow the subsequent steps.
3. Open the sudoers file for editing using visudo command. Make sure you're logged in as root or other sudo user.
$ sudo visudo
4. Locate the line that you want to modify. In our case, it's the line that grants sudo privileges to the sudo group and allows them to run /bin/apt.
5. Replace the current line with the original configuration that you want to restore. For example, if the current line is:
%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) /bin/apt
and you want to revert it back to the default configuration that grants full sudo privileges to the sudo group, it should be:
%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
6. Save and close the sudoers file.
7. Verify the syntax of your sudoers file before exiting visudo. If there are no syntax errors, the changes will be applied.
After making these changes, the sudo configuration will be modified back to the original settings, and the users will have the sudo privileges as they had before the changes were made.
Remember to be careful when modifying the sudoers file, as incorrect configurations can lead to issues with sudo access on your system. Always use visudo to edit the file to avoid syntax errors.
Conclusion
Restricting sudo users to run specific commands is a good way to improve the security of your Linux system. By limiting the commands that sudo users can run, you can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and system damage.
Related Read:
- How To Run Particular Commands Without Sudo Password In Linux
- How To Allow Or Deny Sudo Access To A Group In Linux
- How To Restrict Su Command To Authorized Users In Linux
- Run Commands As Another User Via Sudo In Linux
- How To Prevent Command Arguments With Sudo In Linux
- How To Run All Programs In A Directory Via Sudo In Linux
- How To Restore Sudo Privileges To A User