How to Install and Configure Drupal with Apache on Debian 9
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Debian 12 (Bookworm)
- Debian 11 (Bullseye)
- Debian 9 (Stretch)
On this page
Drupal is a free and open source content management system that can be used to create online content, website and user communities. It is written in PHP language, uses MySQL as a database backends and distributes under the GNU General Public License. Drupal comes with over 17,000 addons to customize its functionality. Drupal runs on all the web server including, Apache, Nginx, IIS, Lighttpd and as backend databases MySQL, MariaDB, MongoDB, SQLite, MS SQL Server, PostgreSQL etc.
In this article, we will demonstrate how to install Drupal 8 on Debian 9 server.
Requirements
- A server running Debian 9 on your system.
- Apache 2.x, MySQL or MariaDB with PDO.
- A non-root user with sudo privileges setup on your server.
1 Getting Started
First, it is recommended to update your system with the latest stable version. You can do this by running the following command:
sudo apt-get update -y
sudo apt-get upgrade -y
Once your system is updated, you will need to install some required packages to your system. You can install all of them by running the following command:
sudo apt-get install wget git unzip nano -y
2 Install LAMP Server
Before you start install of Drupal, you need to have LAMP server (Apache, PHP, and MySQL) installed and configured on your server.
First, start with installing Apache web server with the following command:
sudo apt-get install apache2 -y
After the installation completes, you will need to start Apache service and enable it to start automatically from the next system boot. To do so, run the following command:
sudo systemctl start apache2
sudo systemctl enable apache2
Next, install PHP with required modules by running the following command:
sudo apt-get install php7.0 libapache2-mod-php7.0 php7.0-cli php7.0-mcrypt php7.0-intl php7.0-mysql php7.0-curl php7.0-gd php7.0-soap php7.0-xml php7.0-zip -y
Next, you will need to make some changes in php.ini file:
sudo nano /etc/php/7.0/cli/php.ini
Change the lines as shown below:
memory_limit = 512M date.timezone = UTC cgi.fix_pathinfo=0 upload_max_filesize = 100M post_max_size = 100M
Once you are done, save and close the file.
3 Install and Configure MariaDB
Drupal requires MariaDB/MySQL for database backends, so you will need to install it. You can install it by running the following command:
sudo apt-get install mariadb-server -y
After installation is completes, start MariaDB service and enable it to start automatically at system boot by running the following command:
sudo systemctl start mysql
sudo systemctl enable mysql
Next, you will need to set up security for the database. You can run the following command to secure MariaDB database:
sudo mysql_secure_installation
This script set root password, disable remote root login, remove test database and remove anonymous users as shown below:
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
You already have a root password set, so you can safely answer 'n'.
Change the root password? [Y/n] n
... skipping.
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
After securing the database, Drupal requires an empty MySQL database. So you will need to create a MySQL database and user for the Drupal installation.
First, log in to MySQL shell with the following command:
mysql -u root -p
Enter root password when asked, then create a database for Drupal with the following command:
MariaDB [(none)]>CREATE DATABASE drupaldb;
Next, create a user for drupal database and grant privileges to the drupal database with the following command:
MariaDB [(none)]>GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES on drupaldb.* to 'drupal'@'localhost' identified by 'password';
Next, run the FLUSH PRIVILEGES command reloade the privileges:
MariaDB [(none)]>FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Finally, exit from the MariaDB console with the following command:
MariaDB [(none)]>\q
4 Install and Configure Drupal
First, you will need to download the latest stable version of the Drupal from their official website, otherwise, you can download it directly using the wget command as follows:
wget https://ftp.drupal.org/files/projects/drupal-8.3.4.zip
Afterwards, extract the downloaded zip file and move the extracted Drupal directory to the Apache root directory:
unzip drupal-8.3.4.zip
sudo mv drupal-8.3.4 /var/www/html/drupal
Next, you will need to change some permissions of the drupal directory:
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/drupal
sudo chmod -R 777 /var/www/html/drupal
Next, you will need to create an Apache virtual host file for drupal. To do so, create a new drupal.conf file inside /etc/apache2/sites-available/ directory:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/drupal.conf
Add the following lines:
<VirtualHost *:80> ServerAdmin [email protected] DocumentRoot /var/www/html/drupal ServerName 192.168.15.189 ServerAlias www.example.com <<Directory "/var/www/html/drupal/"> Options FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Order allow,deny allow from all </Directory> ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/drupal-error_log CustomLog /var/log/apache2/drupal-access_log common </VirtualHost>
Save and close the file when you are finished, then enable virtual host with the following command:
sudo a2ensite drupal
You will also need to activate the rewrite module.
sudo a2enmod rewrite
Finally, restart Apache service to apply this changes with the following command:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
5 Access Drupal Web Interface
Everything is now installed and configured. Next, you will need to allow Drupal through UFW firewall. By default, UFW firewall is disabled in Debian 9, so you will need to enable it first.
sudo ufw enable
Then, allow port 80 through UFW firewall by running the following command:
sudo ufw allow 80
Finally, open you web browser and navigate to URL http://192.168.15.189 to start the Drupal web installer. You should see the following page:
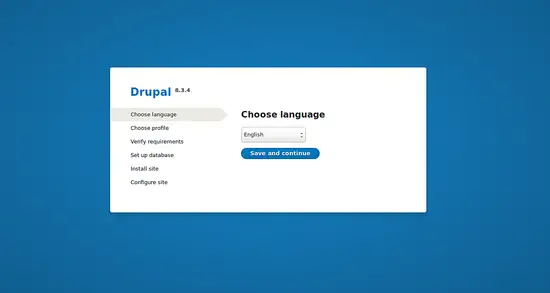
Choose the English language and click on the Save and Continue button, you should see the following image:
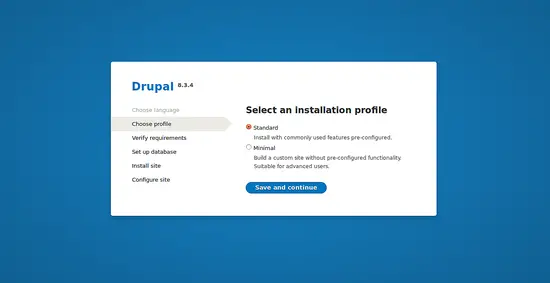
Select an Installation Profile and click on the Save and Continue button, then verify all the requirements and click on the Save and Continue button. You should see the following image:
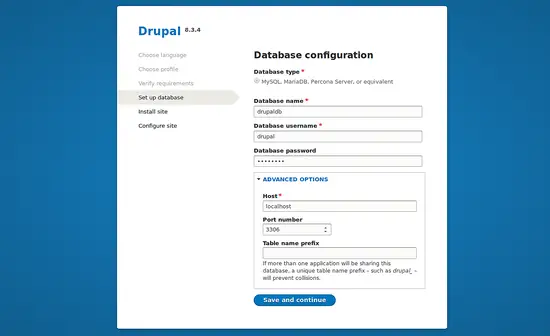
In the Database Configuration page, provide all the required database details like database name, database username and password, database host, then click on the Save and Continue button, you should see the following image:
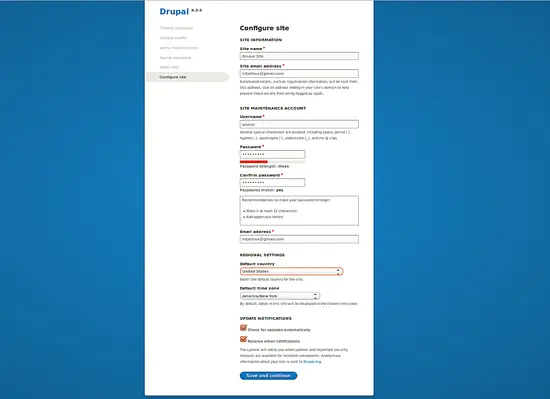
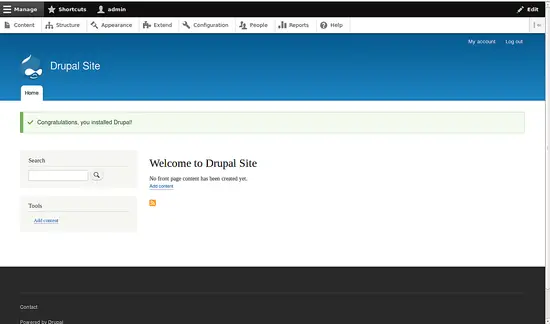
In the Drupal Site Configuration page, provide your site name, admin username and password then click on the Save and Continue button to start installing Drupal. Once Drupal is installed, you should see the Drupal dashboard in the following image:
Conclusion
Congratulations! you have successfully installed and configured Drupal on Debian 9 server. I hope you can now easily create your own website using Drupal. You can visit the Drupal documentation page https://www.drupal.org/docs/8 for more details.